There are multiple Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) types which depends on their layer structure, flexibility, and material. Here below we have listed it for you which are the most common types:
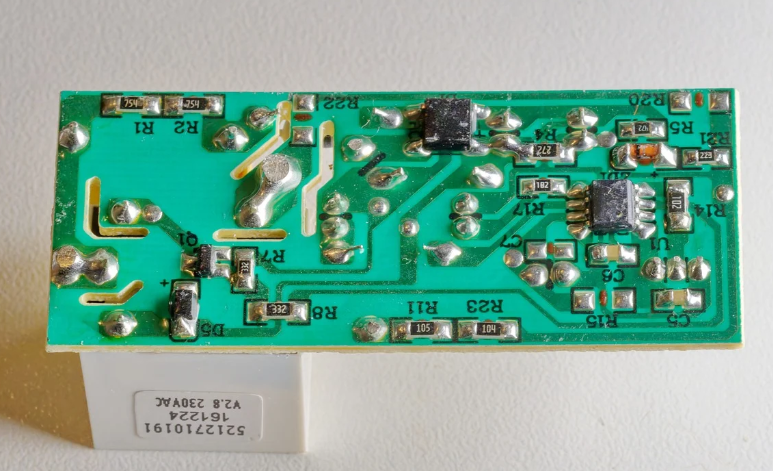
1. Single-Sided PCB
- Structure: One copper layer on one side of the board.
- Use Cases: Low-cost, simple devices like calculators or LED lamps.
- Advantages: Easy to design, low cost.
2. Double-Sided PCB
- Structure: Copper layers on both sides of the board.
- Use Cases: Audio systems, power supplies, and vending machines.
- Advantages: More routing space, suitable for moderate complexity.
3. Multilayer PCB
- Structure: 3 or more layers of copper, separated by insulation.
- Common Variants: 4-layer, 6-layer, 8-layer, up to 40+.
- Use Cases: Laptops, smartphones, medical and aerospace systems.
- Advantages: Compact design, supports high-speed and complex circuits.
4. Rigid PCB
- Material: Solid, non-flexible substrate (like fiberglass).
- Use Cases: TVs, desktops, industrial machines.
- Advantages: Durable, reliable, good for long-term use.
5. Flexible PCB (Flex PCB)
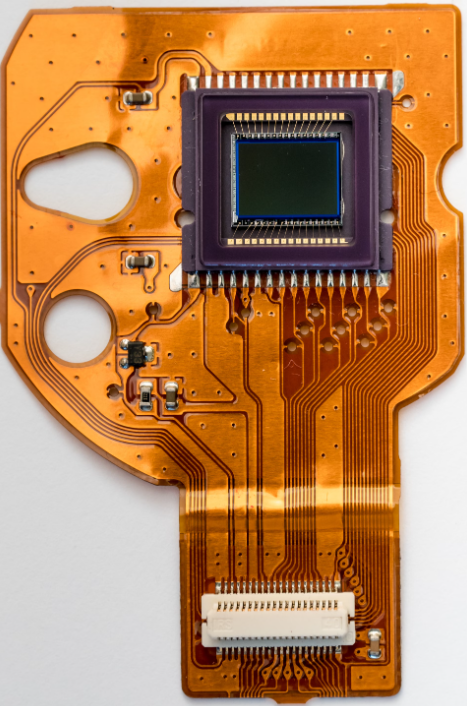
- Material: Flexible plastic-like materials (e.g., polyimide).
- Use Cases: Cameras, foldable phones, medical wearables.
- Advantages: Bendable, space-saving.
6. Rigid-Flex PCB
- Structure: Combination of rigid and flexible sections.
- Use Cases: Military, aerospace, consumer electronics (e.g., foldable phones).
- Advantages: Compact, reliable in high-vibration environments.
7. High-Frequency PCB
- Use Cases: RF communication, satellite, and radar systems.
- Special Materials: PTFE, Rogers materials.
- Advantages: Supports high-speed signals with minimal loss.
8. Aluminum/Metal Core PCB
Summary Table:
| Type | Key Feature | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Sided | One copper layer | Toys, LEDs |
| Double-Sided | Copper on both sides | Power supplies, radios |
| Multilayer | 3+ copper layers | Mobile, medical, servers |
| Rigid | Solid, inflexible | TVs, washing machines |
| Flexible | Bendable | Cameras, wearables |
| Rigid-Flex | Mix of rigid + flexible | Aerospace, smartphones |
| High-Frequency | Handles GHz-level signals | RF devices, communication |
| Aluminum Core | Great for heat dissipation | LED, automotive electronics |
FAQs: Regarding PCB types
1. Which PCB type is ideal for small or compact devices?
HDI PCBs are the best fit for compact gadgets like smartphones and wearables. They allow for tight layouts and support advanced performance without taking up much space.
2. What’s the difference between rigid and flexible PCBs?
Rigid PCBs are solid and keep their shape, commonly used in desktops and TVs. Flexible PCBs, on the other hand, can bend and fold, perfect for dynamic or space-limited designs like cameras and foldables.
3. Why do we use multi-layer PCBs?
Multi-layer boards are great when your circuit needs lots of connections in a small area. They reduce interference and improve overall performance—ideal for complex electronics like laptops or industrial controllers.
4. What is the purpose of a metal core PCB?
These PCBs are built to handle heat. They’re mainly used in applications like LED lights, power equipment, and automotive systems where heat dissipation is critical.
5. Can flexible PCBs handle tough conditions?
Yes, if designed with quality materials, flexible PCBs can last in tough environments. For extra durability and structure, rigid-flex boards combine the best of both worlds.
6. Is the manufacturing process the same for every PCB type?
No, each type requires different steps and materials. Flexible PCBs need bendable substrates, while metal core PCBs involve extra layers for thermal management.
7. How do I decide which PCB type I need?
It depends on your product’s size, complexity, temperature range, and cost. Choosing the right PCB type early helps avoid design changes later on.
DeepSeek vs. ChatGPT: Which AI Chatbot is Better? (2025 Comparison)
The Ultimate List of AI Productivity Tools You Need in 2025
The Most PROFITABLE YouTube Niches in 2025 (Proven!)
The Best YouTube Niches Nobody is Talking About (2025 Edition)
